Definitions of Acute HCV Infection
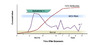
Acute hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is defined as the 6-month period following the acquisition of hepatitis C virus.[1,2,3] This definition does not take into account whether the patient has clinical signs or symptoms of acute hepatitis.[2] The rationale for choosing 6 months as the time period to define acute infection is based on evidence that most individuals who spontaneously clear HCV will do so by 6 months.[4,5,6]
Terminology Related to Acute HCV Infection
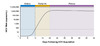
Various terms have been used to refer to acute hepatitis C infection, including acute infection, acute phase infection, very early infection, recent infection, and newly acquired infection. Very early infection typically refers to patients with a positive HCV RNA and documented HCV antibody seroconversion, with this scenario being the most definitive for diagnosing acute HCV infection. Some experts have suggested limiting the terminology for acute HCV infection to acute infection and recent infection:[2]
- Acute Infection: estimated duration of infection less than 6 months
- Recent Infection: estimated duration of infection longer than 6 months, but shorter than 2 years.
 Elbasvir-Grazoprevir Zepatier
Elbasvir-Grazoprevir Zepatier Glecaprevir-Pibrentasvir Mavyret
Glecaprevir-Pibrentasvir Mavyret Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir Harvoni
Ledipasvir-Sofosbuvir Harvoni Ribavirin Copegus, Rebetol, Ribasphere
Ribavirin Copegus, Rebetol, Ribasphere Sofosbuvir Sovaldi
Sofosbuvir Sovaldi Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir Epclusa
Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir Epclusa Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir-Voxilaprevir Vosevi
Sofosbuvir-Velpatasvir-Voxilaprevir Vosevi